A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) geographically connects several nearby LANs (in an area of about fifty kilometers) at high speed. Therefore, a MAN allows two remote nodes to connect and communicate as if they were part of the same Local Area Network.
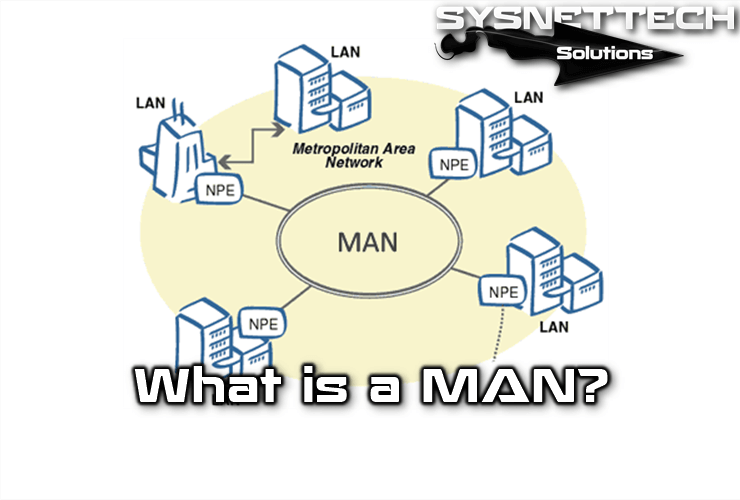
What is a MAN?
MAN consists of switches or routers that are connected by high-speed connections (usually fiber optic cables).
Metropolitan networks have many and diverse applications, the main ones are:
- The deployment of VoIP services in the metropolitan area eliminates the existing cost of these lines by allowing the elimination of “old” traditional analog telephone or ISDN lines.
- Connecting local area networks (LAN)
- The deployment of Wifi Zones without Wireless Backhaul (Femtocell) frees all Wifi channels for access, which in practice represents more than 60% improvement in the connection of Wifi users.
- Computer-to-computer connection.
- Video Surveillance Systems.
- CAD/CAM Transmission.
- Wide Area Network (WAN) Gateways.
Public and Private MAN
A metropolitan network can be private or public. A special MAN example; It can be a large department or administration with buildings spread across cities, transporting all voice and data traffic between buildings through its MAN and directing external information through public operators.
The data can be transferred in different packets or between different buildings on fixed bandwidth channels. Video applications can connect buildings for meetings, simulations, or project collaboration.
An example of a public MAN is the infrastructure that a telecommunications operator has set up to offer broadband services to its customers located in this geographic area.
Components
The components of the metropolitan network where the user requests the applications and services provided by the network are:
- Workstations
- Central Computers
- Personal Computers
Network Nodes
They are the devices responsible for providing services to jobs that are part of the network. The main functions are:
- The temporary storage of information to be transmitted until the transmission channel is released.
- Only accept its own, filtering information circulating over the network.
- Conversion of network information into business information, eights.
- Obtaining access rights to the transmission medium.
Cabling System
It consists of a cable used to connect network nodes and workstations.
Communication Protocols
These are the rules and procedures used in a network to communicate between nodes. Different communication levels are defined in the protocols. Thus, metropolitan networks support level 1 and part of level 2 by serving higher-level protocols that follow the OSI hierarchy for open systems.
Applications
Possible network applications are possible, such as message processing systems (MHS), File Management, Access and Transfer (FTAM) and EDI.
Network Services
The following is a classification of possible services offered by metropolitan networks:
- Non-Connection Oriented Services
It allows data transfer without establishing a previous connection.
- Connection-Oriented Services
A connection must be established before the user data is migrated.
- Isochronous Services (Concurrent) Services
They are used when there are strict bandwidth requirements, such as streaming certain audio and video services. Some applications require the continuous transfer of information (concurrently) at regular intervals. In this case, although there is a new FDDI-II standard that supports concurrent traffic, not all technologies support such applications, such as FDDI.
Advantages of Installing a MAN
The reasons for establishing an institutional-level metropolitan network or accessing a public network with the same features are summarized below:
Band Width
The high bandwidth required for large computers and shared network applications is the main reason for using metropolitan networks instead of local area networks.
Network Nodes
It allows more than 500 network access nodes and is very effective for public and private environments with many jobs.
Network Extension
It allows a diameter of about 50 km, depending on the distance between the network nodes of the cable type used and the technology used. This diameter is considered to be sufficient to cover a metropolitan area.
Distance Between Nodes
It allows distances between several nodes of access nodes, depending on the type of cable. These distances are thought to be sufficient to connect different buildings in a metropolitan area or private campus.
Real-Time Traffic
It guarantees minimum network access times that allow the inclusion of synchronous services required for real-time applications where it is important for certain messages to pass over the network, even if the network load is high.
Voice, Data and Video Integration
In addition to minimum access times, synchronized services require bandwidth reservations; audio and video traffic. Therefore, these networks are best suited for multimedia traffic environments, but not all metropolitan networks support traffic (information transfer at certain intervals) at the same time.
High Availability
Availability refers to the percentage of time that the network operates without errors. It has automatic fault recovery mechanisms that allow the network to be recovered after normal operation. Any malfunction in an access node or cable is quickly detected and isolated. Suitable for MAN networks, air traffic control, warehouse supply, banks and other commercial applications where network failure is serious.
High Reliability
Reliability refers to the error rate while the network is running. It is understood that the error rate is the number of bad bits transmitted over the network. In general, the error rate for optical fiber is lower than that of equal length copper wire. The error rate not detected by the error detection mechanisms is around 10-20. This feature allows metropolitan area networks to operate in environments where errors such as air traffic control can be disastrous.
High Security
Fiber optics offer a safe method because it is not possible to read or change the optical signal without physically disconnecting the connection. Breaking a cable and installing non-network mechanisms means a temporary connection drop.
Noise Immunity
In critical locations where the network is exposed to significant electromagnetic interference, fiber optics provide a noiseless communication tool.
Related Articles
♦ Switching
♦ What is Cisco?
♦ What is a VPN?
♦ What is VLAN?
♦ What is Ethernet?