Token Ring is a circular network connecting computers. The network packet travels through the ring, facilitating information exchange. In this way, computers can exchange information.
What is the Token Ring Network and Its History?
IBM company is the basis for the most basic history of the Token Ring network. In the 1970s, IBM created this network technology as an alternative to Ethernet. Hence, the IEEE 802.5 document published in 1985 refers to the first Token Ring standard. The document refers to transmitting information, not connecting computers. Additionally, the document relates to sharing information, not connecting computers.
E. E. Newhall designed the first one in 1969. IBM published the Token-Ring topology in March 1982. Continuing network development, speed increased to 4 Mbps in 1988. Additionally, they introduced the second-gen Token Ring-II with rates up to 16 Mbps. Also, it used coaxial cable and fiber optics.
New LAN cabling costs became essential. Thus, old Token Ring-II networks with twisted pair wires required rewiring.
When the token ring first came to be, big companies became interested. They liked its secure and stable solution. This network uses a token system to keep data safe.
When Ethernet became famous, token networks lost favor. People found them costly and complicated to set up. So, they switched to Ethernet, which is more straightforward.
During the 1990s, Ethernet networks gained popularity and overshadowed the Token Ring. As a result, in the 2000s, users widely adopted Ethernet for most networks.
How Does Token Ring Work?
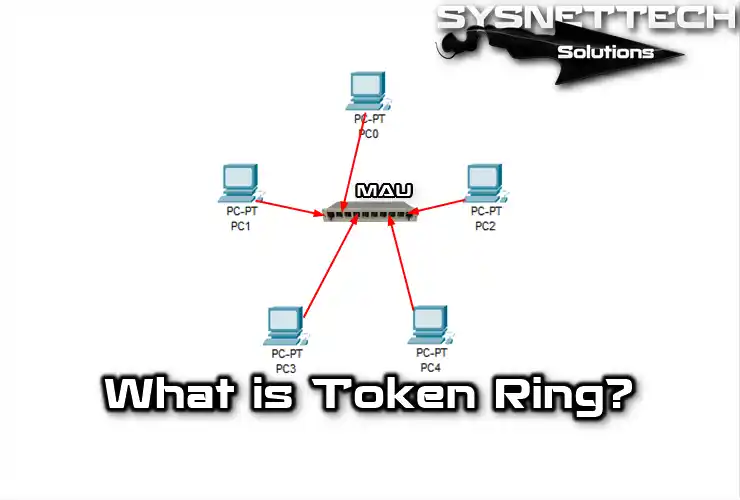
The token network has a logical ring designed as a physical star. So, it’s intended as a physical star.
Unlike Ethernet networks, these networks are deterministic. The main reason is that the device controls medium access. Thus, only one computer can send data at a time. Data packets determine which computer can share data, achieving this control. Moreover, data packets do this control by deciding which computer can share data.
MAU (Multistation Access Unit) connects computers in a star shape in the Token Ring network. This hardware connects computers like physical star topology. But, it logically works as a ring topology.
Lobes connect computers to the MAU; one lobe’s max cable length is 22.5 or 100 meters. Additionally, if the network expands, the length can be up to 2.5 km using repeaters.
Token networks expand through the Ring-Out and Ring-In ports of MAUs; up to 33 devices can connect. Also, extensive networks like campuses use fiber cables.
This network has an advanced priority system for specific users. Moreover, the system prioritizes higher-priority computers to use the web more frequently. You can manage an MAU device over the serial interface with the SNMP protocol.
Key Features of Token Ring
Let’s examine the secure Token Ring features preferred by big companies. Still, modern networks offer better efficiency and security.
- Fast Data Transfer: Thanks to this network technology, you can quickly transfer data. But, each device only sends its data once it receives the token.
- Low Data Losses: Token-based structure reduces losses. Hence, devices avoid direct connection for prevention.
- High Security: This network works on a simple idea. Data moves with the permission-based transmission. Thus, each device can only send data if it receives the token. In this case, data transmission in the network is relatively high security.
- Low Latency: Token Ring is a network protocol for super-fast, low-latency data transmission. Moreover, each device expects tokens within specific timeframes.
- Equal Distribution: The device shares tokens equally with others. This helps in a reasonable transfer of data between devices.
- Flexible Expansion: In token networks, you can expand flexibly. With ring logic, users configure these networks. Adding new devices is effortless.
- Error Detection System: This system has a unique technology. It can discover and repair mistakes during data transfer.
Cable Structure in Token Networks
Networks commonly use cable: shielded/unshielded twisted pair. Or coaxial or fiber optic cables achieve higher data transfer rates.
A star wiring center can detect and correct faults if the cable breaks or gets damaged in this network. In such cases, this solution resolves the problem.
The network fixes a problem in the ring, enabling it to continue operating. Additionally, computers connect to the ring network using RIUs (Ring Interface Units).
Working Logic of Token Technology
Token networks use different mechanisms for error detection. One such mechanism involves designating a network computer as an active monitor. Also, this helps ensure smooth network operation.
This computer is a central time information source for computers in another ring. So, it performs the maintenance function effectively.
The active monitoring computer is any network computer. Its task is to cut the constant roaming of ring frames. Additionally, it helps maintain efficient network performance.
If this process fails, it blocks other computers from forwarding frames. So, the network may become blocked as well. The monitor detects edges and extracts them from the web. Then, it creates a new token as well.
Advantages of Token Ring Network
- It does not need routing.
- The wiring required is low.
- The network is easy to grow.
- It can send data to more stations by amplifying the signal.
Disadvantages of Token Ring Network
- It is susceptible to failures that may occur in the network.
- Due to a fault in the ring, all network operation ceases.
- It is difficult as the software configurations of each node are more complex.
Related Articles
1) What is a Network with PCs?
2) What is the IPX Protocol in Networking?
3) What is the SLIP Protocol in Networking?
4) Mainframe Definition
5) Frame Relay Definition


Thankyou for the article. I’m looking some help on migrating token ring based applications to ethernet. Can we consult you?