The gateway enables the interconnection of networks.
It connects through different protocols and architectures at all communication levels. People commonly refer to these devices as a computer.
What Does a Gateway Do?
The primary purpose of gateways is to convert information. They transform from the protocol used in one network to the protocol used in the target network.
Gateways differ from Bridges in functionality. They are more than just conduits for information between systems without conversion.
These devices change and send information packets. They ensure compatibility with the target system’s syntax. Additionally, they operate at the Application layer of the OSI model.
Connecting computer LANs can be challenging in various ways. But, it is possible to interconnect different networks with TCP/IP and SNA architecture.
It does not provide routing functions in the LAN but only sends packets to read data traffic.
When it receives a packet from an area, it translates the packet from the format used on the web. It does this in a standard form among gateways. It then sends the packet to another one. The target device receives it and translates it into the format used on its LAN.
How the Gateway Works?
The gateway routes computers belonging to a local area LAN connected to it. It does this to gain access to an external LAN. Additionally, it often performs IP address conversion.
This address translation function enables computers on the local area network to access the Internet. It does so by externally sharing a single Internet connection and a single IP address.
In home environments, people use ADSL or cable modem routers as gateways. They connect the home’s local network to the Internet. However, they cannot connect two separate LANs with different protocols. Instead, they can only connect two independent networks using NAT.
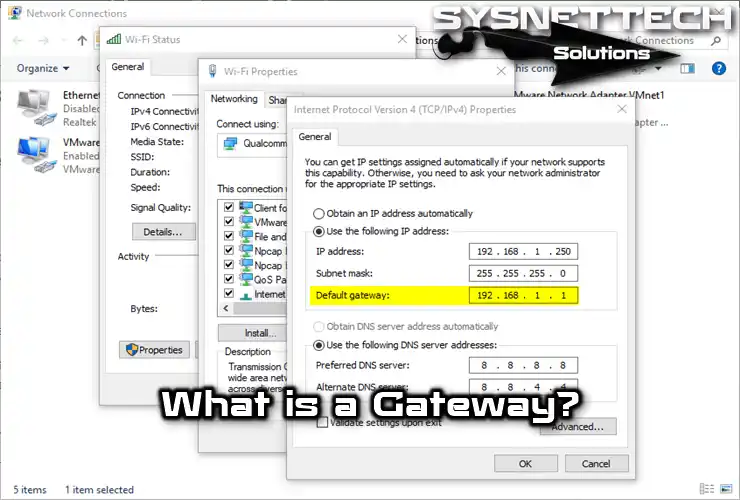
The IP block in your Internet modem’s settings usually determines the address of a gateway. For example, if your modem’s IP block is 192.168.1.0/24, the gateway address of clients on the LAN will be the modem’s IP address. This is because the modem’s IP address will be 192.168.1.1.
A server computer is configured as it requires at least two adapters. Thus, you will configure one adapter for the local area and the other for the target one.
In this case, the default gateway server will be the default route assigned to the local area. Its function is to send the packet over the default route. It does so by sending any packages that it does not know through which interface the incoming packets will be sent. Also, it processes packets that device routes cannot define.
LAN Bridge Types
There are two types of gateways: network adapters or software or external hardware.
Network Adapter or Software Based System
These devices are computers equipped with adapters of different protocols. They correspond to interconnected segments of different LAN types.
This type allows other software protocols. They are usually assigned to computers to translate data traffic.
External Hardware-Based System
Hardware-based gateway devices translate protocols. Specialized intelligent devices allow communication between equipment that have different architectures. Moreover, these equipment are capable of functioning in various operating system environments.