Safe entry is key in computer networks. The Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) is one first ways in this area. It gives a simple, far-away link method. In the 1980s, it was made to work with the Point-to-Point Rule (PPP).
It sends the user’s login details to the network for checking. Sadly, it sends this data as clear words. This causes significant safety weaknesses.
Because of this, PAP is not enough in today’s online world. Its simple style made it common in older systems. But safer other choices are now needed.
Knowing PAP shows the growth of checking. It also shows the need for strong answers against new Internet dangers.
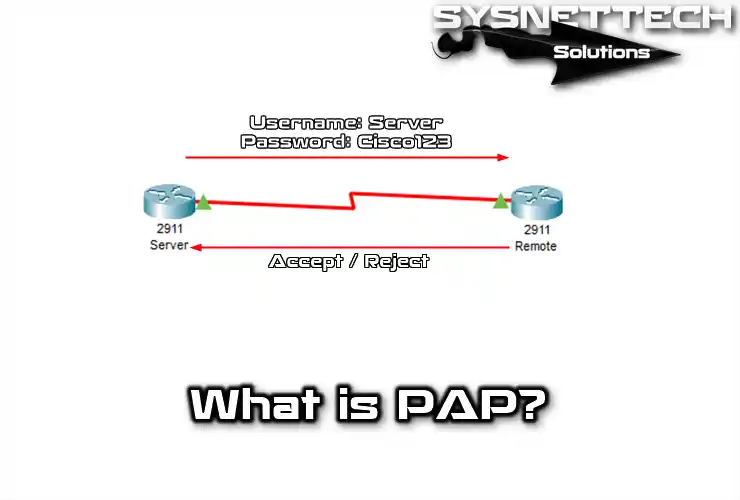
What Is the PAP Protocol Providing Network Authentication?
PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) is a way to make sure remote connections are safe. So, this method confirms your identity when you want to connect to an ISP network.
PAP system checks if you’re allowed to use certain things. It was first explained in 1984. However, it works with something called PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol).
This system sends messages in a simple code that is not secure. That means the connection is not safe. PAP can manage if the remote access server doesn’t have a more robust method.
The way PAP works is like a friendly greeting. However, old SLIP systems send passwords as plain text, which is unsafe. You can use TTLS authentication as an easy solution to make things more secure.
How Does PAP Work?
The people who make computer stuff created PAP technology to help two devices share essential information. They also said it’s a particular way of talking that keeps things secret and safe.
When one device gets messages from another device in a PC network, it checks if the connecting device is active and asks for important info. This helps the remote machine make sure that everything is okay and can be trusted.
PAP is an old way to verify identity. First, the Client shares login info in a packet. Then, it keeps sending requests until it gets proof.
Clearly, the PAP protocol follows a simple rule: It works on a straightforward concept.
- Client Request: Firstly, users want to access networks or systems. Then, they ask for credentials like usernames and passwords.
- Credentials Submission: The user sends credentials to the server first. Yet, this method sends info without encryption. Therefore, username and password data can be seen on the network.
- Authentication: The server checks credentials against its records. If correct, it lets the user in.
So, the reason why the Client is not secure is that it sends credentials in plain text. In this case, bad actors can easily spy on and attack it.
PAP Protocol Advantages and Disadvantages
Authentication is vital in PC network communication. PAP is one way, but it has pros and cons, like any protocol.
Advantages
- Simplicity
It is a straightforward authentication method to use. However, they will provide remote access; they must enter their username and password. Thus, it is simple for both clients and servers.
- Universality
PAP is good with many network protocols; no issues. Users use it on dial-up and older Wi-Fi networks. Thus, it works with existing infrastructures for authentication.
- Ease of Debugging
A plus is easy debugging; users quickly find problems. This helps with faster troubleshooting when issues arise.
Disadvantages
- Security Issues
The biggest problem with this protocol is the security issues. Simply, it opens the door to attackers by not encrypting the information.
- Storage of Passwords
Servers store user passwords to help users access their accounts. But this can be dangerous for system security. If someone shouldn’t get in, they might mess up essential accounts.
- A Backward Compatible Protocol
A long time ago, developers created PAP. But now, it doesn’t meet today’s security needs. That’s why you should use better methods.
PAP Protocol Usage Areas
Users have employed the PAP protocol in various applications. These include both past and present use cases. Here are some examples:
- Dial-Up Connections
Users widely used this protocol in dial-up network connections at the time. In this type of transmission, they used telephone lines and thus provided access to the Internet.
However, users would use modems to connect to different places to confirm their dial-up credentials. These devices send info to ISPs, allowing approved access. During that time, people widely used the PAP protocol to establish the basic structure of the web.
- DSL Modems
DSL modem technology uses PAP to provide broadband web access. Users verify their identity by entering their username and password. So, these devices then establish a connection by sending this info to the ISP server.
- Wireless Networks
Some wireless networks authenticate the user with PAP. That is, it controls users who want to access these networks. However, they prefer the PAP method less because there are safer methods today.
- Private Networks
Administrators can use PAP to reach out to users in specific private network setups. This enables authorized individuals to connect and access the network as needed.
Differences Between PAP and CHAP
PAP uses a simple way to log in. This means the remote system uses a username and password to prove who it is.
CHAP makes sure each login is unique. It uses a more innovative and safer way to control things. This includes the names of the Client and server using a one-way secret code method. So, CHAP is much safer than PAP because everything constantly changes.
| Features | PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) | CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Provides a low level of security. Transmits the username and password in clear text. | Provides a higher level of security. Passwords are different for each session. |
| Password Storage | Store user information in clear text on the server. | Does not store user information in clear text on the server. |
| Session Persistence | Does not maintain session persistence. The username and password are sent with each request. | Ensures sessions remain connected. Credentials are not resent. |
| Error Detection | There is no error detection or correction mechanism. The session is terminated immediately if incorrect information is provided. | Provides error detection and correction features. If you enter incorrect information, you will be given multiple attempts. |
| Security Level | Lower security. | Higher security. |
| Communication Method | Sends the username and password in plain text. | Communicates using the challenge and response method. |
| Usage Areas | Used for simple tasks that do not require security. | Widely used in areas with high security needs. |
| Session Duration | Uses a single session because the session is short. | The session persists continuously. No reauthentication is required between sessions. |
Conclusion
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) was the basis of online talking. But, it is now longer enough for today’s safety rules.
Its simple and easy use were big good points. But sending passwords as clear words is a considerable danger.
As tools get better, safety problems also change. So, secure ways are now needed. For example, new rules like CHAP are a lot safer.
Groups must change to these safe checking ways. In the end, we can make network safety the best.
Also, we can guard against bad entry and data leaks. This way, we can make a safer online place for all people.
