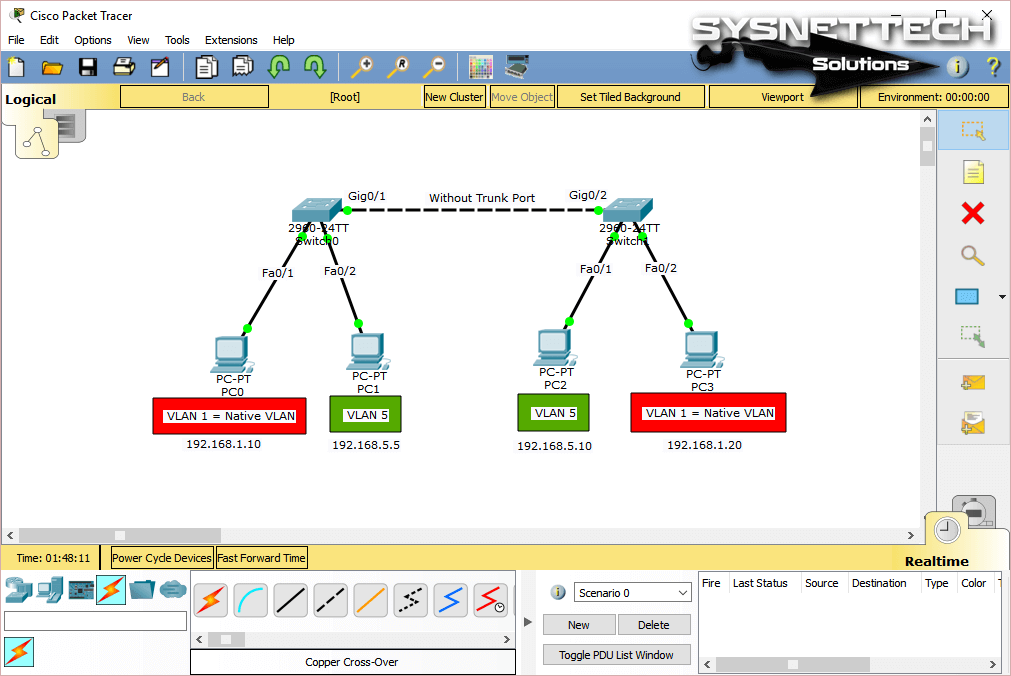
A native VLAN is a VLAN without a tag. VLAN1 is automatically on when you set up switches. Since it’s not tagged, computers connected to different switches can talk to each other without any extra steps.

What is the Native VLAN?
It passes 802.1Q and ISL tags on the ports we configure as trunk connections.
But let’s say we did not make a trunk connection between the two Switches. In this case, we only allow computers on Native VLAN, that is, VLAN1, to communicate.
The reason why we make a trunk connection between two Switches is that the access ports cannot pass tags.
How Does Native VLAN Work?
The main VLAN is not affected and can move data packets between the two switches without any problem. That’s why VLAN1 is automatically on when you set up switches.
Because VLAN1 isn’t tagged, any computer or device linked to the switch can chat without needing to be in a VLAN. However, it can’t talk to other devices in the VLAN.
For inter-VLAN data flow, the inter-VLAN operation is performed on the routers. If your network has Layer 3 switches, they can also help with VLAN routing.
Using VLAN1 isn’t safe for network security. So, it’s best to switch out VLAN1 for something more secure.
Working Logic of Native VLAN (VLAN1) Structure
Let’s look at the network layout shown below and check out how VLAN1 works. Understanding this is really important for knowing how the network works.
Pinging between VLAN1 member PCs will be successful. However, ping between VLAN5 member PCs will fail.
If you’re in VLAN1, you can’t talk to someone in VLAN5. This separation ensures network security and efficiency.
What are The Differences Between 802.1Q and ISL Tags?
There are two different ways to label and identify VLAN traffic: 802.1Q and ISL. The big difference between them is that 802.1Q is a standard anyone can use, while ISL is made just by Cisco.
802.1Q is the most common way to label virtual LAN traffic. Almost all network gear supports it. It puts a 4-byte tag on Ethernet frames with the ID and some other details. This tag helps switches separate different groups even if they’re using the same physical network.
ISL, on the other hand, is made only by Cisco. It adds a 26-byte header to Ethernet frames, including the ID and more details like source and destination MAC addresses. ISL only works with Cisco gear and isn’t a standard others can use.
How Do They Affect VLAN1 Configuration?
When setting up VLANs, both 802.1Q and ISL can be used to make them and let them talk to each other. However, with Cisco switches, ISL only works on older ones with IOS software version 12.0 or before. Newer switches with IOS version 12.1 or later only support 802.1Q.
When you’re making LAN groups, it’s essential to make sure both ends of a trunk link use the same tagging way. If one end uses 802.1Q and the other uses ISL, they can’t talk to each other.
To sum it up, 802.1Q and ISL are two different ways to tag VLAN traffic. 802.1Q is widely used and open to everyone, while ISL is just for Cisco. You can use both for groups, but both ends of a trunk link need to use the same tagging way.
VLAN1 Working Principle ⇒ Video
You can watch the video below to review the working logic of VLAN1 between two Cisco SWs using Packet Tracer. Also, subscribe to our YouTube channel to support us!
Final Word
In this article, we have examined what VLAN1 is and how it works by default when configuring VLANs in Switches. Thanks for following us!