Static NAT is a one-to-one assignment between the internal address and the external address. This NAT type allows external devices to initiate connections to internal devices through a statically assigned public address. For example, only a specific internal global address can be assigned so that the user can access an internal web server from an external network.
Understanding Static NAT
With Static, you can bring a specific computer or device on the local network to the Internet. You can map a device with a private IP address of this NAT type to a single IP address.
In short, you must do this manually when you add a route to your device because this structure is only used to configure a specific device.
In more comprehensive network topologies, you can use NAT in different scenarios. For example, you can hide the IP block that you use for local network security.
In Cisco or any Router model, you can use both the CLI prompt and the GUI management interface to configure NAT.
The logic of NAT is as follows;
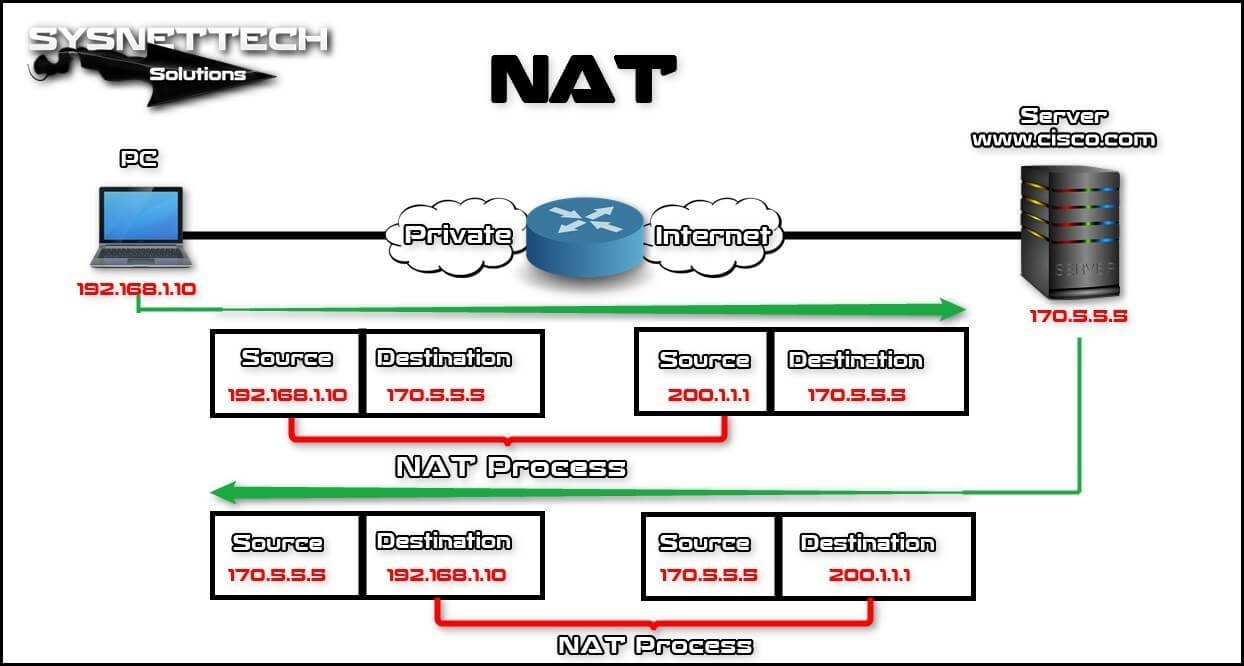
Static address translation works with the same logic as the structure in the image above. However, routes are added manually. In such a case, the static conversion applies to a computer that will access the external network from the local network.
How Does It Work?
To better understand the working logic of NAT, you can create and configure a topology with the Packet Tracer software, as in the image below.

In the NAT translations above, the computer with the Local IP address 192.168.10.10 was converted to a Global IP address assigned by the ISP or configured for the external network when trying to access the Internet.
If more than one IP address is allocated by the ISP, Dynamic NAT operation is performed on the Router. Otherwise, organizations that have a single Public IP can bring certain PCs or devices on their local networks to the Internet.
In the network topology above, it cannot access the Internet if there is no NAT record for a second computer. So we need to add a record for this computer as well.
In NAT statistics, Inside Local refers to private networks. Global networks are referred to as Inside Global.
Configuration ⇒ Video
With Packet Tracer, you can watch the video below to configure Static NAT on network topology and also subscribe to our YouTube channel to support us!
Final Word
In this article, we have basically discussed what Static Network Address Translation is and how it works. Thanks for following us!